Vertical Circulation: Stairs
Design Consideration And Awareness
The safety of all users is paramount when designing stairs in any setting. However, the daily use of stairs and the climbing or physical coordination required, can play a positive role in the development of gross motor skills of young children. This is particularly important for children with sensory, physical or cognitive difficulties, who may use the stairs, with and without the assistance of an adult.
The clear width of a stairs, which is measured between handrails, will depend on the location of the setting and the number of users. The clear width should be a minimum of 1200mm. The total rise of a single flight should be no more than 1800mm and contain no more than 12 steps. Winders such as those in a spiral staircase or tapered steps are not suitable in an ELC setting as they can create a sense of insecurity and confusion for some users.
Contrasting colours between the steps of the staircase and the staircase frame and walls can help a person with sensory, physical or cognitive challenges to identify steps and changes in level or gradient, thereby simplifying the visual environment, which is beneficial for people with vision difficulties. Lighting is very important on internal stairs so that they can be used safely.
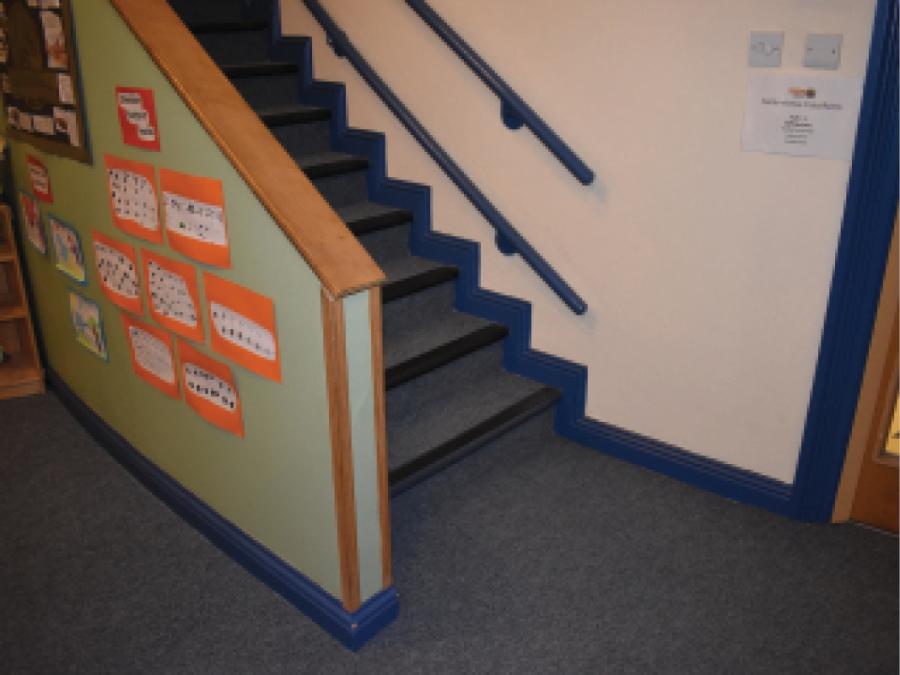

18. Tigers Childcare, Blanchardstown, Dublin
Tigers Childcare, Blanchardstown, Dublin.
Design features
- Lower level handrail provides support for children and people of lower stature.
- Open and clearly visible stairs provides a positive space within the setting.
Design tip
- Greater colour contrast between steps and floor would help with visibility.
- Handrails should extend 300mm beyond the bottom of the stairs.
- Ensure a door located at the bottom of a staircase opens in to avoid risk of injury.
- Using a different contrast nosings on the first and last step of the stairs would help to
identify the top and bottom of the stairs.
It should be noted that certain hazard-warning surfaces that provide high visual and tactile contrast, may be disorientating for a person with sensory, physical or cognitive difficulties and should therefore be given careful consideration. For example, a sharp contrast in flooring colour can be perceived as a step or hole by people who may have perceptual problems. This may place the person at greater risk of a fall.
The provision of an additional handrail between 600 – 750mm above the pitch line is essential for children. This will also provide support for people of smaller stature. Both handrails should contrast in colour to the background walls so that they are clearly visible and easily identified.
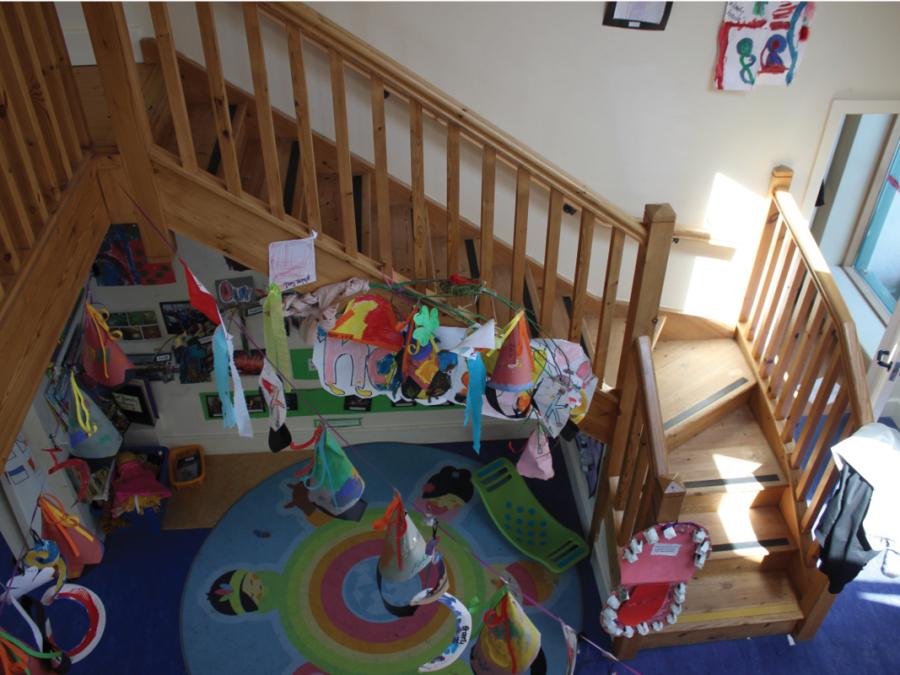

19. Ballindereen Community Childcare and Education Centre, Ballinderreen, County Galway
Ballindereen Community Childcare and Education Centre, Ballinderreen, County Galway.
Design features
- Stairs to a mezzanine level, designed and used as a natural part of the setting helps children develop gross motor skills and competencies.
Design tip
- Lower level additional handrail may help some smaller children.
- Handrails must extend 300mm beyond the end of the stairs.
Note: Refer to the Universal Design Guidelines for Homes in Ireland -Section 2 (2015) and Building for Everyone – Booklet 3 (2014) for more information regarding stairs.
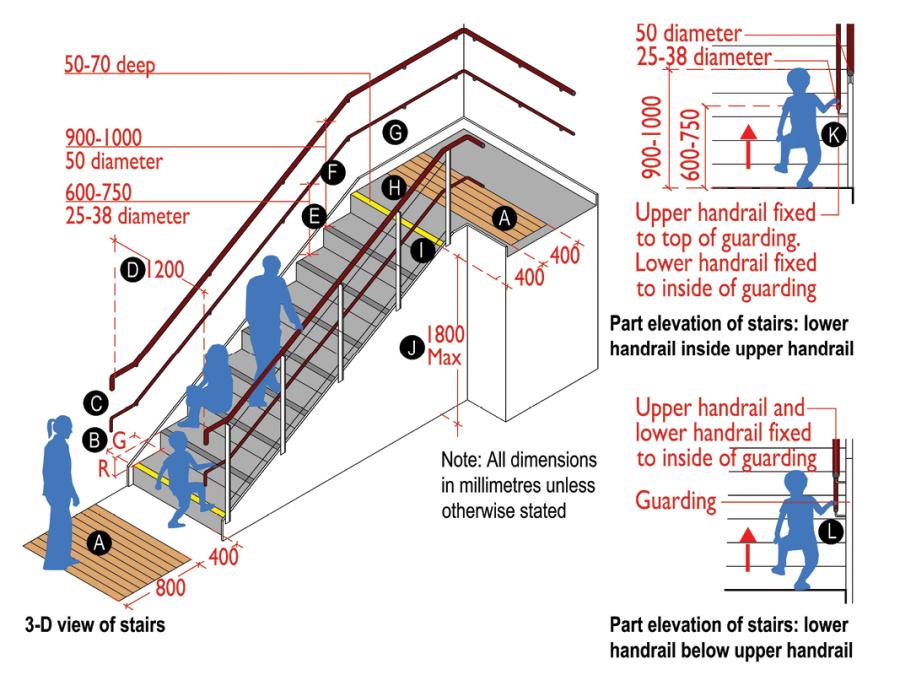
Technical sketch 6: Indicative internal stairs
A. Optional 800mm deep corduroy tactile warning surface indicator (TWSI) at the top and bottom of stairs. The TWSI can be reduced to 400mm (as shown on the top landing) when a conscious turn is needed to reach the step.
B. Steps with 150-180mm rise (height) and 300-450mm going (depth).
C. Handrails provided on both sides of the stairs. Handrails extend 300mm into top and bottom landing and turn down by 150mm or turned into wall.
D. 1200mm minimum clear width between upper handrails.
E. Lower handrail fixed 600-750mm above pitch line. Handrail diameter 25-38mm.
F. Upper handrail fixed 900-1100mm above landing and 900-1000mm above pitch line. Handrail diameter to be between 40-50mm.
G. Handrails should be continuous on landings on both sides of the stairs.
H. Steps with 50-70mm deep contrast nosings extending across the width of the steps.
I. Guarding should not provide footholds or be climbable by children (e.g. avoid horizontal rails). Guarding should be designed so that a 100mm sphere would not pass through any part of the guarding.
J. The total rise between landings in any flight should not exceed 1800mm or 12 steps.
K. Where the upper handrail sits on top of the guarding the lower handrail will need to be fixed inside the guarding. This may reduce the clear width of the stairs.
L. Where the upper handrail is fixed inside the guarding the lower handrail can also be fixed inside the guarding in line with upper handrail above.
Universal Design Guidance
- Locate and design stairs so they can play a positive role in the development of gross motor skills and the competencies of small children.
- For centre based settings, the clear width of the stairs, which is measured between handrails should be a minimum of 1200mm.
- For centre based settings, the total rise of a single flight should be no more than 1800mm and contain no more than 12 steps.
- Use colour contrast between the steps and the walls to highlight stairs.
- Be aware that certain hazard-warning surfaces may be disorientating for people with sensory, physical or cognitive difficulties and should therefore be given careful consideration.
- Install an additional handrail between 600 – 750mm above the pitch line for children and people of smaller stature.
- Handrails should contrast in colour or tone to the background walls so that they are clearly visible and easily identified.
- Handrails must extend 300mm beyond the end of the stairs.




